同步操作将从 程序员大彬/Java-learning 强制同步,此操作会覆盖自 Fork 仓库以来所做的任何修改,且无法恢复!!!
确定后同步将在后台操作,完成时将刷新页面,请耐心等待。
JDBC定义了连接数据库的接口规范,每个数据库厂商都会提供具体的实现,JDBC是一种典型的桥接模式。
public class javaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
String URL="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/imooc?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8";
String USER="root";
String PASSWORD="tiger";
//1.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得数据库链接
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
//3.通过数据库的连接操作数据库,实现增删改查(使用Statement类)
Statement st=conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=st.executeQuery("select * from user");
//4.处理数据库的返回结果(使用ResultSet类)
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("user_name")+" "
+rs.getString("user_password"));
}
//关闭资源
rs.close();
st.close();
conn.close();
}
}
Hibernate建立在POJO和数据库表模型的直接映射关系上。通过POJO我们可以直接操作数据库的数据。相对而言,Hibernate对JDBC的封装程度比较高,我们不需要编写SQL,直接通过HQL去操作POJO进而操作数据库的数据。
Mybatis是半自动映射的orm框架,它需要我们提供POJO,SQL和映射关系,而全表映射的Hibernate只需要提供POJO和映射关系。
Hibernate编程简单,需要我们提供映射的规则,完全可以通过IDE实现,同时无需编写SQL,开发效率优于Mybatis。此外,它提供缓存、级联、日志等强大的功能,
Hibernate与Mybatis区别:
Hibernate是全自动,而Mybatis是半自动。 Hibernate是全表映射,可以通过对象关系模型实现对数据库的操作,拥有完整的JavaBean对象与数据库的映射结构来自动生成sql。而Mybatis仅有基本的字段映射,对象数据以及对象实际关系仍然需要通过手写sql来实现和管理。
Hibernate数据库移植性较好。 Hibernate通过它强大的映射结构和hql语言,大大降低了对象与数据库的耦合性,而Mybatis由于需要手写sql,因此与数据库的耦合性直接取决于程序员写sql的方法,如果sql不具通用性而用了很多某数据库特性的sql语句的话,移植性也会随之降低很多,成本很高。
Hibernate拥有完整的日志系统,Mybatis则欠缺一些。 Hibernate日志系统非常健全,涉及广泛,包括:sql记录、关系异常、优化警告、缓存提示、脏数据警告等;而Mybatis则除了基本记录功能外,功能薄弱很多。
sql直接优化上,Mybatis要比Hibernate方便很多。 由于Mybatis的sql都是写在xml里,因此优化sql比Hibernate方便很多,解除了sql与代码的耦合。而Hibernate的sql很多都是自动生成的,无法直接维护sql;写sql的灵活度上Hibernate不及Mybatis。
Mybatis提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
使用xml构建SqlSessionFactory,配置信息在mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--定义别名-->
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="role" type="com.tyson.pojo.Role"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--默认使用development数据库构建环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!--采用JDBC事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--配置数据库连接信息-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdemo?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--定义映射器-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="RoleMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class SqlSessionFactoryUtil {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
//类线程锁
private static final Class CLASS_LOCK = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.class;
/**
* 私有化构造器
*/
private SqlSessionFactoryUtil() {}
public static SqlSessionFactory initSqlSessionFactory() {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (CLASS_LOCK) {
if(sqlSessionFactory == null) {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
}
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
public static SqlSession openSqlSession() {
if(sqlSessionFactory == null) {
initSqlSessionFactory();
}
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
SqlSession是接口类,扮演门面的作用,真正处理数据的是Executor接口。在Mybatis中SqlSession的实现类有DefaultSqlSession和SqlSessionManager。
映射器的实现方式有两种:通过xml方式实现,在mybatis-config.xml中定义Mapper;通过代码方式实现,在Configuration里面注册Mapper接口。建议使用xml配置方式,这种方式比较灵活,尤其当SQL语句很复杂时。
xml文件配置方式实现Mapper
public interface RoleMapper {
public Role getRole(@Param("id") Long id);
}
映射xml文件RoleMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper">
<!--SQL列的别名与pojo的属性一样,则SQL查询的结果会自动映射到pojo-->
<select id="getRole" parameterType="long" resultType="com.tyson.pojo.Role">
SELECT id, role_name as roleName, note FROM role WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
测试类
import com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper;
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
import com.tyson.util.SqlSessionFactoryUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
@Slf4j
public class RoleTest {
@Test
public void findRoleTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
Role role = roleMapper.getRole(1L);
if(role != null) {
log.info(role.toString());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
}
Java方式实现Mapper
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
public interface RoleMapper1 {
@Select(value="SELECT id, role_name as roleName, note from role where id = #{id}")
public Role getRole(@Param("id") Long id);
}
在Mybatis全局配置文件注册Mapper,有三种方式。
<!--定义映射器-->
<!--resource:引入类路径下的资源
URL:引入网络或磁盘的资源
class:引用注册接口
1.有sql映射文件,映射文件名必须和接口同名,并且放在与接口同一目录下;
2.没有sql映射文件,所有的sql都是基于注解写在接口上。
-->
<mappers>
<!--方式一:通过映射文件注册 Mapper-->
<!--<mapper resource="RoleMapper.xml"/>-->
<!-- 方式二:通过mapper元素的class属性可以指定一个Mapper接口进行注册 -->
<!-- 基于映射文件的接口。映射文件名必须和接口同名,并且放在与接口同一目录下-->
<!--<mapper class="com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper"/>-->
<!-- 基于注解的接口。没有sql映射文件,所有的sql都是基于注解写在接口上-->
<!--<mapper class="com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper1"/>-->
<!-- 方式三:通过package元素将指定包下面的所有Mapper接口进行注册
批量注册 :基于映射文件的接口与映射文件必须在同一个包下
name:包的全类名 -->
<package name="com.tyson.mapper"/>
</mappers>
作用是生成SqlSessionFactory,构建完毕则作用完结,生命周期只存在于方法的局部。
创建SqlSession,每次访问数据库都需要通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession。故SqlSessionFactory应存在于Mybatis应用的整个生命周期。
会话,相当于JDBC的Connection对象,生命周期为请求数据库处理事务的过程。
作用是发送SQL,返回结果或执行SLQ修改数据库数据,它的生命周期在一个SqlSession事务方法之内。其最大的作用范围和SqlSession相同。
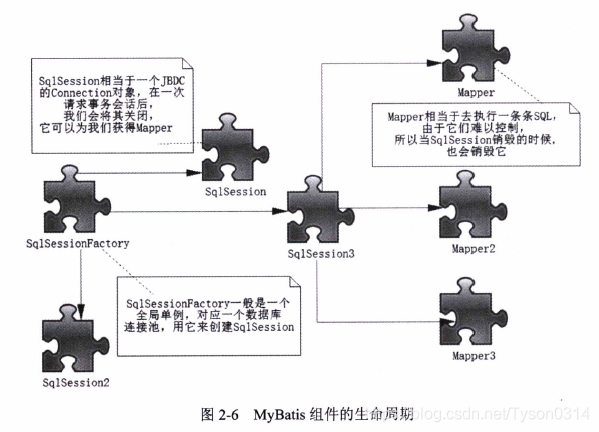
Mybatis全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml的层次结构顺序不能颠倒,否则在解析xml文件会产生异常。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties/><!--属性-->
<settings><!--设置-->
<setting name="" value=""/>
</settings>
<typeAliases></typeAliases><!--别名-->
<typeHandlers></typeHandlers><!--类型处理器-->
<objectFactory></objectFactory><!--类型工厂-->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor=""></plugin>
</plugins>
<!--默认使用development数据库构建环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!--采用JDBC事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--配置数据库连接信息-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<databaseIdProvider></databaseIdProvider>
<!--定义映射器-->
<mapper></mapper>
</configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdemo?serverTimezone=UTC
username=root
password=ad1234
<!--定义别名-->
<typeAliases>
<!--<typeAlias alias="role" type="com.tyson.pojo.Role"/>-->
<!--自动扫描,默认别名为首字母小写的类名-->
<package name="com.tyson.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
参考自:关于mybatis中typeHandler的两个案例
类型处理器,作用是将参数从javaType转化为jdbcType,或者从数据库取出结果时把jdbcType转化成javaType。typeHandler和别名一样,分为系统定义和用户自定义。Mybatis系统定义的typeHandler就可以实现大部分的功能。
public TypeHandlerRegistry() {
this.register((Class)Boolean.class, (TypeHandler)(new BooleanTypeHandler()));
this.register((Class)Boolean.TYPE, (TypeHandler)(new BooleanTypeHandler()));
this.register((JdbcType)JdbcType.BOOLEAN, (TypeHandler)(new BooleanTypeHandler()));
this.register((JdbcType)JdbcType.BIT, (TypeHandler)(new BooleanTypeHandler()));
this.register((Class)Byte.class, (TypeHandler)(new ByteTypeHandler()));
this.register((Class)Byte.TYPE, (TypeHandler)(new ByteTypeHandler()));
......
}
假如需要将日期以字符串格式(转化成毫秒数)写进数据库,此时可以通过自定义typeHandler来实现此功能。
role表
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`note` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`reg_time` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL,
`users` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
Role实体类
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class Role {
private Long id;
private String roleName;
private String note;
private Date regTime;
//setter和getter
@Override
public String toString() {
return "id: " + id + ", roleName: " + roleName + ", note: " + note + ", regTime: " + regTime; //+ ", users: " + users.get(0);
}
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedJdbcTypes;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedTypes;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
@Slf4j
@MappedJdbcTypes({JdbcType.VARCHAR})
@MappedTypes({Date.class})
public class MyDateTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Date> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, Date date, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
log.info("预编译语句设置参数: " + date.toString());
preparedStatement.setString(i, String.valueOf(date.getTime()));
}
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
log.info("由列名 " + s + " 获取字符串:" + resultSet.getLong(s));
return new Date(resultSet.getLong(s));
}
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
log.info("由下标 " + i + " 获取字符串:" + resultSet.getLong(i));
return new Date(resultSet.getLong(i));
}
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
log.info("通过callbleStatement下标获取字符串");
return callableStatement.getDate(i);
}
}
<!--类型处理器-->
<typeHandlers>
<!--<typeHandler jdbcType="VARCHAR" javaType="java.util.Date" handler="com.tyson.typeHandler.MyDateTypeHandler"/>-->
<!--扫描包-->
<package name="com.tyson.typeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper">
<resultMap id="roleMap" type="role">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="long" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="role_name" property="roleName" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="note" property="note" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="reg_time" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="regTime" javaType="java.util.Date"/>
</resultMap>
<!--使用resultMap进行结果映射, 用typeHandler对reg_time字段进行转化-->
<select id="getRole" parameterType="long" resultMap="roleMap">
SELECT id, role_name, note, reg_time FROM role WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<!--取regTime值也可以只配置typeHandler,即#{regTime,typeHandler=com.tyson.typeHandler.MyDateTypeHandler}-->
<insert id="insertRole" parameterType="role">
INSERT into role(id, role_name, note, reg_time)
VALUES(#{id}, #{roleName}, #{note}, #{regTime,javaType=Date, jdbcType=VARCHAR})
</insert>
</mapper>
Mybatis内部提供了两个转化枚举类型的typeHandler:org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler和org.apache.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler。EnumTypeHandler使用枚举字符串名称作为参数传递,EnumOrdinalTypeHandler使用整数下标作为参数传递。
下面通过EnumOrdinalTypeHandler实现性别枚举。
public enum Sex {
MALE(1, "男"), FEMALE(2, "女");
private int id;
private String name;
private Sex(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public static Sex getSex(int id) {
if(id == 1) {
return MALE;
} else if(id == 2) {
return FEMALE;
} else {
return null;
}
}
//setter和getter
}
StudentMapper.java
public interface StudentMapper {
public Student findStudent(int id);
public void insertStudent(Student student);
}
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap = "studentMap">
select id, name, sex from student where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
insert into student(name, sex) values(#{name},
#{sex, typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler})
</insert>
</mapper>
测试类
import com.tyson.entity.Sex;
import com.tyson.entity.Student;
import com.tyson.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.tyson.util.SqlSessionFactoryUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
@Slf4j
public class StudentTest {
@Test
public void findStudentTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s = studentMapper.findStudent(3);
if(s != null) {
log.info(s.toString());
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
@Test
public void insertStudentTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("tyson");
s.setSex(Sex.MALE);
studentMapper.insertStudent(s);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
}
插入的sex字段为INTEGER,测试结果如下:
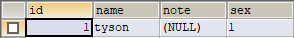
通过EnumTypeHandler实现性别枚举只需修改StudentMapper.xml相应的typeHandler,修改如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler"/>-->
<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap = "studentMap">
select id, name, sex from student where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
insert into student(name, sex) values(#{name},
#{sex, typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler})
</insert>
</mapper>
插入的sex字段为VARCHAR类型,测试结果如下:
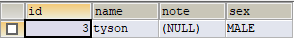
SexEnumTypeHandler类的定义。
import com.tyson.entity.Sex;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@Slf4j
public class SexEnumTypeHandler implements TypeHandler<Sex> {
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, Sex sex, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
log.info("预编译语句设置参数: " + i);
preparedStatement.setInt(i, sex.getId());
}
@Override
public Sex getResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
log.info("由列名 " + s + " 获取字符串:" + resultSet.getString(s));
int id = resultSet.getInt(s);
return Sex.getSex(id);
}
@Override
public Sex getResult(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
log.info("由下标 " + i + " 获取字符串:" + resultSet.getInt(i));
int id = resultSet.getInt(i);
return Sex.getSex(id);
}
@Override
public Sex getResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
@Override
public Sex getResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
int id = callableStatement.getInt(i);
return Sex.getSex(id);
}
}
}
mybatis-config.xml增加SexEnumTypeHandler的定义
<typeHandlers>
<!--扫描包-->
<package name="com.tyson.typeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler"/>-->
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler"/>-->
<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="com.tyson.typeHandler.SexEnumTypeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap = "studentMap">
select id, name, sex from student where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
insert into student(name, sex) values(#{name},
#{sex, typeHandler=com.tyson.typeHandler.SexEnumTypeHandler})
</insert>
</mapper>
测试结果如下:
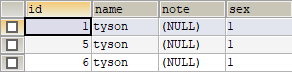
当Mybatis在构建一个结果返回时,都会使用ObjectFactory去构建POJO,可以定制自己的对象工厂。一般使用默认的ObjectFactory即可,默认的ObjectFactory为org.apache.ibatis.reflection.factory.DefaultObjectFactory提。
配置环境可以注册多个数据源,每一个数据源分为两部分的配置:数据库源的配置和数据库事务的配置。
<!--默认使用development数据库构建环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!--采用JDBC事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="autoCommit" value="false"/>
</transactionManager>
<!--配置数据库连接信息-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
(1)JDBC,使用JDBC管理事务,独立编码时常常使用;
(2)MANAGED,使用容器方式管理事务,在JNDI数据源中常用;
(3)自定义,由使用者自定义数据库管理方式,适用于特殊应用。
(1)UNPOOLED,非连接池数据库
(2)POOLED,连接池数据库
(3)JNDI数据源
(4)自定义数据源
Mybatis数据库事务由SqlSession控制,我们可以通过SqlSession提交或回滚。
@Test
public void insertRoleTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
Role role = new Role();
role.setId(2L);
role.setNote("hi");
role.setRoleName("teacher");
roleMapper.insertRole(role);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
| 元素 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | 和Mapper命名空间的组合是唯一的 | 命名空间和id组合不唯一,则抛异常 |
| parameterType | 类的全路径或者别名 | 基本数据类型,JavaBean,Map等 |
| resultType | 基本数据类型或者类的全路径,可使用别名(需符合别名规范) | 允许自动匹配的请况下,结果集将通过JavaBean的规范映射,不能和resultMap同时使用 |
| resultMap | 自定义映射规则 | Mybatis最复杂的元素,可以配置映射规则、级联、typeHandler等 |
autoMappingBehavior不为NONE时,Mybatis会提供自动映射的功能,只要返回的列名和JavaBean的属性一致,Mybatis就会帮助我们回填这些字段。实际上大部分数据库规范使用下划线分割单词,而Java则是用驼峰命名法,于是需要使用列的别名使得Mybatis能够自动映射,或者在配置文件中开启驼峰命名方式。
<!--SQL列的别名与pojo的属性一样,则SQL查询的结果会自动映射到pojo-->
<select id="getRole" parameterType="long" resultMap="roleMap">
SELECT id, role_name as roleName, note FROM role WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
自动映射可以在setting元素中配置autoMappingBehavior属性值设定其策略。包含三个值:
默认值是PARTIAL,默认情况下可以做到当前对象的映射,使用FULL是嵌套映射,性能会下降。
如果数据库是规范命名的,即每个单词用下划线分隔,而POJO是驼峰式命名的方式,此时可设置mapUnderscoreToCamelCase为true,这样就可以实现从数据库到POJO的自动映射了。
public List<Role> findRoleByCondition(@Param("roleName") String roleName, @Param("note")String note);
RoleMapper.xml
<select id="findRoleByCondition" resultMap="roleMap">
SELECT id, role_name, note FROM role
WHERE role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%')
</select>
将参数组织成JavaBean,通过getter和setter方法设置参数。
public class RoleParam {
private String roleName;
private String note;
public String getRoleName() {
return roleName;
}
public void setRoleName(String roleName) {
this.roleName = roleName;
}
public String getNote() {
return note;
}
public void setNote(String note) {
this.note = note;
}
}
接口RoleMapper
public List<Role> findRoleByParams2(RoleParam roleParam);
RoleMapper.xml
<select id="findRoleByParams2" parameterType="com.tyson.pojo.RoleParam" resultMap="roleMap">
SELECT id, role_name, note FROM role
WHERE role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%')
</select>
参数个数多于5,建议使用JavaBean方式。
<resultMap id="roleMap" type="role">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="long" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="role_name" property="roleName" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<!--定义结果类型处理器标识-->
<result column="note" property="note" typeHandler="com.tyson.typeHandler.MyStringTypeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findRoleByParams1" resultMap="roleMap">
SELECT id, role_name, note FROM role
WHERE role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%')
</select>
执行插入之后会返回一个整数,表示插入的记录数。parameterType 为 role(mybatis-config.xml 定义的别名)。
<insert id="insertRole" parameterType="role">
INSERT into role(id, role_name, note) VALUES(#{id}, #{roleName}, #{note})
</insert>
部分内容参考自:insert主键返回 selectKey使用
设计表的时候有两种主键,一种自增主键,一般为int类型,一种为非自增的主键,例如用uuid等。
role表指定id字段为自增字段,对应的Role实体类提供getter和setter方法,便可以使用Mybatis的主键回填功能。通过keyProperty指定主键字段,并使用useGeneratedKeys告诉Mybatis这个主键是否使用数据库内置策略生成。
<!--useGeneratedKeys:默认false,使MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键
keyProperty:默认值unset,用于设置getGeneratedKeys方法或selectKey子元素返回值将赋值到哪个属性中-->
<insert id="insertRoleUseGeneratedKeys" parameterType="role" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
INSERT into role(role_name, note) VALUES(#{roleName}, #{note})
</insert>
传入的role无需设置id,Mybatis在插入记录时会自动回填主键。
@Test
public void insertRoleUseGeneratedKeysTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
Role role = new Role();
role.setNote("hello");
role.setRoleName("worker");
roleMapper.insertRoleUseGeneratedKeys(role);
log.info(role.toString());
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
也可以通过selectKey设置主键回填。
<insert id="insertRole" parameterType="role">
<!--selectKey会将 SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()的结果放入到传入的pojo的主键;
keyProperty 对应的pojo中的主键的属性名;
order设置为BEFORE,先执行selectKey语句(SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()),然后执行插入语句;
order设置为AFTER,先执行插入语句,然后执行selectKey语句;
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID():得到刚insert 进去记录的主键值,只适用与自增主键;
resultType:主键类型
-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="long" order="AFTER">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
INSERT into role(role_name, note) VALUES(#{roleName}, #{note})
</insert>
假设增加如下需求,当表role没有记录时,则插入第一条记录时id设为1,否则取最大的id加2,设置为新的主键,这个时候可以使用selectKey来处理。
<insert id="myInsertRole" parameterType="role">
<!--order为BEFORE,selectKey语句在insert语句插入之前执行-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="java.lang.Long" order="BEFORE">
select if(max(id) is null, 1, max(id) + 2) as newId from role
</selectKey>
INSERT into role(id, role_name, note) VALUES(#{id}, #{roleName}, #{note})
</insert>
selectKey标签的语句会被先执行,然后把查询到的id放到role对象。
@Test
public void myInsertRoleTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
Role role = new Role();
role.setNote("hello");
role.setRoleName("worker");
roleMapper.myInsertRole(role);
log.info(role.toString());
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
假设主键是VARCHAR类型,以uuid()方式生成主键。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.CustomerMapper">
<insert id="insertCustomer" parameterType="com.tyson.pojo.Customer">
<!--order为BEFORE,uuid()在insert语句插入之前执行-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="java.lang.String" order="BEFORE">
select uuid()
</selectKey>
insert customer(id, name) values(#{id}, #{name})
</insert>
</mapper>
测试类。
import com.tyson.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.tyson.pojo.Customer;
import com.tyson.util.SqlSessionFactoryUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
@Slf4j
public class InsertCustomerTest {
@Test
public void insertCustomer() {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
session = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
CustomerMapper customerMapper = session.getMapper(CustomerMapper.class);
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setName("tyson");
customerMapper.insertCustomer(customer);
session.commit();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
session.rollback();
} finally {
if(session != null) {
session.close();
}
}
}
}
update和delete元素用于更新记录和删除记录。插入和删除记录执行完成会返回一个整数,表示插入或删除几条记录。
<update id="updateRole" parameterType="role">
update role set
role_name = #{roleName},
note = #{note}
where id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteRole" parameterType="long">
delete from role where id = #{id}
</delete>
测试类
@Test
public void updateRole() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
Role role = new Role();
role.setId(2L);
role.setRoleName("actor");
role.setNote("fired");
roleMapper.updateRole(role);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
@Test
public void deleteRole() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
roleMapper.deleteRole(8L);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
resultMap元素主要包括以下元素:
<resultMap id="" type="">
<constructor>
<idArg/>
<arg/>
</constructor>
<id/>
<result/>
<association property=""/>
<collection property=""/>
<discriminator javaType="">
<case value=""></case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
constructor元素用于配置构造方法。对于没有无参构造方法的POJO,可用constructor元素进行配置。
<constructor>
<idArg column="id" javaType="int"/>
<arg column="role_name" javaType="string"/>
</constructor>
Mybatis中级联分为三种:association、collection和discriminator。
以学生和学生证为例,学生和学生证是一对一的关系,在Student建立一个类型为StudentCart的属性sc,这样便形成了级联。
public class Student {
int id;
String name;
Sex sex;
StudentCard sc;
//setter和getter
}
public class StudentCard {
int id;
int sid;
String note;
//setter和getter
}
在StudentCartMapper.xml中提供findStudentCardByStudentId方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentCardMapper">
<resultMap id="scMap" type="studentCard">
<id property="id" column="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result property="note" column="note"/>
<result column="sid" property="sid"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudentCardByStudentId" parameterType="int" resultMap="scMap">
select id, note, sid from student_card where sid = #{sid}
</select>
</mapper>
在StudentMapper里使用StudentCardMapper进行级联。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler"/>-->
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler"/>-->
<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="com.tyson.typeHandler.SexEnumTypeHandler"/>
<!--select指定特定的SQL去查询,column指定传给SQL的参数,如果是多个参数,则用逗号分隔-->
<association property="sc" column="id"
select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentCardMapper.findStudentCardByStudentId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap = "studentMap">
select id, name, sex from student where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
insert into student(name, sex) values(#{name},
#{sex, typeHandler=com.tyson.typeHandler.SexEnumTypeHandler})
</insert>
</mapper>
测试association级联。
@Test
public void findStudentTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try{
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s = studentMapper.findStudent(1);
log.info(s.toString());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
测试结果:
22:37:54.931 [main] INFO com.tyson.StudentTest - id: 1, name: tyson, sex: MALE, cardId: 10086
一个学生有多门课程,这是一对多的级联。建立Lecture的POJO记录课程和StudentLecture表示学生课程表,StudentLecture里有一个类型为Lecture的属性lecture,用来记录学生成绩。
StudentLecture和Lecture类:
public class StudentLecture {
int id;
int studentId;
Lecture lecture;
int grade;
//setter和getter
}
public class Lecture {
int id;
String lectureName;
//setter和getter
}
Student类添加一个List类型的属性。
public class Student {
int id;
String name;
Sex sex;
StudentCard sc;
List<StudentLecture> studentLectureList;
//setter和getter
}
StudentMapper.xml使用collection对Student和StudentLecture做一对多的级联。
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumOrdinalTypeHandler"/>-->
<!--<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler"/>-->
<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="com.tyson.typeHandler.SexEnumTypeHandler"/>
<!--select指定特定的SQL去查询,column指定传给SQL的参数,如果是多个参数,则用逗号分隔-->
<association property="sc" column="id"
select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentCardMapper.findStudentCardByStudentId"/>
<!--select指定特定的SQL去查询,column指定传给SQL的参数,如果是多个参数,则用逗号分隔-->
<collection property="studentLectureList" column="id"
select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentLectureMapper.findStudentLectureByStudentId"/>
</resultMap>
StudentLectureMapper.xml需要使用association对StudentLecture和Lecture做一对一的级联。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentLectureMapper">
<resultMap id="studentLectureMap" type="com.tyson.entity.StudentLecture">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result property="grade" column="grade"/>
<association property="lecture" column="lecture_id"
select="com.tyson.mapper.LectureMapper.findLectureById"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudentLectureByStudentId" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentLectureMap">
select sid as studentId, grade, lecture_id from student_lecture where sid = #{sid}
</select>
</mapper>
LectureMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.LectureMapper">
<select id="findLectureById" parameterType="int" resultType="lecture">
select id, name as lectureName from lecture where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
测试类
@Test
public void findStudentTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try{
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s = studentMapper.findStudent(1);
log.info(s.toString());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
测试结果如下:
10:46:33.916 [main] INFO com.tyson.StudentTest - id: 1, name: tyson, sex: MALE, cardId: 10086, studentLectureList: StudentLecture{studentId=1, lecture=id: 1, lectureName: math, grade=90}, StudentLecture{studentId=1, lecture=id: 2, lectureName: physics, grade=78},
鉴别器级联是在特定的条件下去使用不用的POJO。比如可以通过学生信息表的sex属性进行判断关联男生健康指标或者女生的健康指标。新建MaleStudentHealth.java和FemaleStudentHealth.java,存储男生女生的健康信息。新建MaleStudent.java和FemaleStudent.java,继承自Student.java类。
public class MaleStudentHealth {
int height;
//setter和getter
}
public class MaleStudent extends Student {
List<MaleStudentHealth> maleStudentHealthList;
//setter和getter
}
StudentMapper.xml如下,在discriminator元素通过sex字段的值判断是男生还是女生。当sex=1时,引入maleStudentMap的resultMap,这个resultMap继承自studentMap,使用collection对MaleStudent和MaleStudentHealth做一对多的级联。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.tyson.entity.Student">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex" typeHandler="com.tyson.typeHandler.SexEnumTypeHandler"/>
<!--select指定特定的SQL去查询,column指定传给SQL的参数,如果是多个参数,则用逗号分隔-->
<association property="sc" column="id" select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentCardMapper.findStudentCardByStudentId"/>
<!--select指定特定的SQL去查询,column指定传给SQL的参数,如果是多个参数,则用逗号分隔-->
<collection property="studentLectureList" column="id"
select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentLectureMapper.findStudentLectureByStudentId"/>
<discriminator javaType="int" column="sex">
<case value="1" resultMap="maleStudentMap"/>
<case value="2" resultMap="femaleStudentMap"/>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="maleStudentMap" type="maleStudent" extends="studentMap">
<collection property="maleStudentHealthList" column="id" select="com.tyson.mapper.MaleStudentHealthMapper.findMaleStudentHealthByStuId"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="femaleStudentMap" type="femaleStudent" extends="studentMap">
<collection property="femaleStudentHealthList" column="id" select="com.tyson.mapper.FemaleStudentHealthMapper.findFemaleStudentHealthByStuId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap = "studentMap">
select id, name, sex from student where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
测试结果如下:
16:39:14.123 [main] INFO com.tyson.StudentTest - MaleStudent{maleStudentHealthList=MaleStudentHealth{height=170}, MaleStudentHealth{height=172}, id=1, name='tyson', sex=MALE, sc=studentCard: 10086, studentLectureList=[StudentLecture{studentId=1, lecture=id: 1, lectureName: math, grade=90}, StudentLecture{studentId=1, lecture=id: 2, lectureName: physics, grade=78}]}
级联的优势在于能够方便快捷地获取数据,但是每次获取数据时,所有级联数据都会取出,每一个关联都会多执行一次SQL,这样会造成SQL执行过多性能下降。
假如我们通过传入id查找学生信息,然后打印出学生证信息,代码如下:
@Test
public void findStudentTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try{
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student s = studentMapper.findStudent(1);
log.info("***********获取学生证信息***********");
log.info("学生的学生证信息:" + s.getSc().toString());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
测试结果如下,所有级联数据都会被加载出来。

为了解决这个问题可以采用延迟加载的功能。首先打开延迟加载的开关。
<settings>
<!--打开延迟加载的开关-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
重新运行测试代码,结果如下:

由图可知,当我们查找学生信息时,会同时查出健康信息,当访问学生课程时,会同时把学生证信息查出。原因是Mybatis默认是按层级延迟加载的,如下图所示:
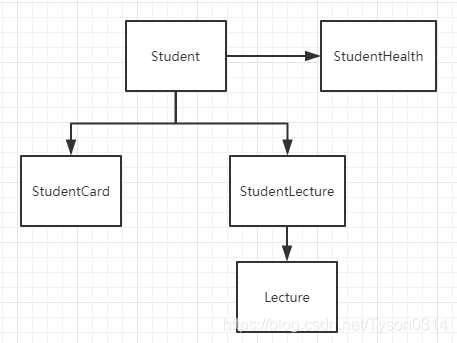
当加载学生信息时,会根据鉴别器找到健康的信息。而当我们访问学生课程时,由于学生证和学生课程是一个层级,也会访问到学生证信息。通过设置全局参数aggressiveLazyLoading可以避免这种情况。aggressiveLazyLoading默认值是true,使用层级加载的策略,设置为false则会按照我们的需要去延迟加载数据。
<settings>
<!--打开延迟加载的开关-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--按需加载-->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
测试结果如下,此时会根据我们的需要加载数据,不需要的数据不会被加载。

aggressiveLazyLoading是全局的设置,不能指定哪个属性可以立即加载,哪个属性可以延迟加载。假如我们在查找学生信息时,很多情况下需要同时把学生课程成绩查出,此时采用即时加载比较好,多条SQL同时发出,性能高。我们可以在association和collection元素加入属性值fetchType(取值为lazy和eager),便可以实现局部延迟加载的功能。(需先设置aggressiveLazyLoading为false)
StudentMapper.xml设置学生证和健康信息延时加载,学生课程即时加载。
<association property="sc" column="id" fetchType="lazy" select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentCardMapper.findStudentCardByStudentId"/>
<collection property="studentLectureList" column="id" fetchType="eager" select="com.tyson.mapper.StudentLectureMapper.findStudentLectureByStudentId"/>
<resultMap id="maleStudentMap" type="maleStudent" extends="studentMap">
<collection property="maleStudentHealthList" column="id" fetchType="lazy" select="com.tyson.mapper.MaleStudentHealthMapper.findMaleStudentHealthByStuId"/>
</resultMap>
StudentLectureMapper.xml设置课程信息即时加载。
<resultMap id="studentLectureMap" type="com.tyson.entity.StudentLecture">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result property="grade" column="grade"/>
<association property="lecture" column="lecture_id" fetchType="eager"
select="com.tyson.mapper.LectureMapper.findLectureById"/>
</resultMap>
测试代码:
public void findStudentTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try{
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
studentMapper.findStudent(1);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
测试结果如下,可以看到有三条SQL被执行,查询学生信息,学生课程和课程信息。当我们访问延迟加载对象时,它才会发送SQL到数据库把数据加载回来。
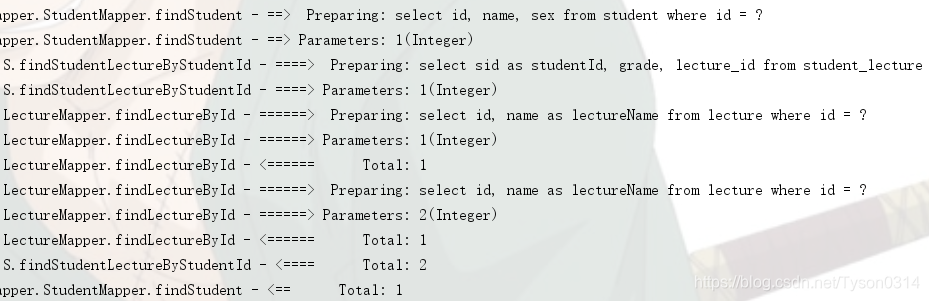
Mybatis的动态SQL主要包括以下几种元素。
| 元素 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| if | 单条件分支判断 |
| choose(when、otherwise) | 相当于Java的switch、case |
| foreach | 在in语句等列举条件常用 |
| trim(where、set) | 用于处理SQL拼装问题 |
if元素和test属性联合使用。
<select id="getRoleByRoleName" parameterType="string" resultMap="roleMap">
select id, role_name, note, reg_time FROM role where 1=1
<if test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
and role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
</if>
</select>
choose、when和otherwise类似于Java的switch、case和default。
<select id="findRoles" parameterType="role" resultMap="roleMap">
select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
and role_name = #{roleName}
</when>
<when test="note != null and note != ''">
and note = #{note}
</when>
<otherwise>
and id != 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
where元素解析时会自动将第一个字段的and去掉。
<select id="findRoles" parameterType="role" resultMap="roleMap">
select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role
<where>
<if test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
and role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
</if>
<if test="note != null and note != ''">
and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
测试结果:
11:42:16.301 [main] DEBUG c.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper.findRoles - ==> Preparing: select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role where note like concat('%', ?, '%')
11:42:16.404 [main] DEBUG c.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper.findRoles - ==> Parameters: hi(String)
使用trim也可以达到同样的效果。prefix代表语句前缀,prefixOverrides代表需要去掉的字符串。
<select id="findRoles" parameterType="role" resultMap="roleMap">
select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
and role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
</if>
<if test="note != null and note != ''">
and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%')
</if>
</trim>
</select>
当在 update 语句中使用if标签时,如果前面的if没有执行,则或导致逗号多余错误。使用set标签可以将动态的配置 SET 关键字,并剔除追加到条件末尾的任何不相关的逗号。使用 if+set 标签修改后,如果某项为 null 则不进行更新,而是保持数据库原值。
<update id="updateRole" parameterType="role">
update role
<set>
<if test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
role_name = #{roleName},
</if>
<if test="note != null and note != ''">
note = #{note},
</if>
<if test="regTime != null">
reg_time = #{regTime}
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
测试结果如下,最后一个逗号被去掉了。
11:39:37.975 [main] DEBUG c.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper.updateRole - ==> Preparing: update role SET role_name = ?, note = ? where id = ?
11:39:38.111 [main] DEBUG c.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper.updateRole - ==> Parameters: actor(String), fired(String), 2(Long)
foreach用于遍历元素,支持数组、List和Set接口的集合。
<insert id="batchInsertRole" parameterType="java.util.List">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="java.lang.Long" order="AFTER">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
insert into role(role_name, note, reg_time) values
<!--mapper接口参数没有使用@Param指定参数名称,则collection名称默认为list-->
<foreach collection="roleList" item="role" separator=",">
(#{role.roleName}, #{role.note}, #{role.regTime,javaType=Date, jdbcType=VARCHAR})
</foreach>
</insert>
<select id="findRolesInIds" parameterType="java.util.List" resultMap="roleMap">
select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role
<if test="ids != null">
where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
RoleMapper.java
//List没有使用@Param指定参数名称,则对应Mapper.xml中的collection名称为list
public void batchInsertRole(@Param("roleList") List<Role> roleList);
public List<Role> findRolesInIds(@Param("ids") int[] ids);
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| collection | 数组、List或Set接口 |
| item | 当前元素 |
| index | 当前元素在集合的下标 |
| open/close | 用什么符号将集合元素包装起来 |
| separator | 间隔符 |
当进行模糊查询时,对于MySQL数据库,我们经常会用concat函数用%和参数连接。对于Oracle则是用||符号连接。这样不同的数据库便需要不同的实现。有了bind元素,就不用考虑使用何种数据库语言,只要使用Mybatis的语言即可与所需参数相连,提高其移植性。
<select id="findRoles" parameterType="role" resultMap="roleMap">
<bind name="roleName_pattern" value="'%' + roleName + '%'"/>
<bind name="note_pattern" value="'%' + note + '%'"/>
select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
and role_name like #{roleName_pattern}
</if>
<if test="note != null and note != ''">
and note like #{note_pattern}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
测试结果:
15:05:21.798 [main] DEBUG c.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper.findRoles - ==> Preparing: select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role where role_name like ? and note like ?
15:05:21.946 [main] DEBUG c.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper.findRoles - ==> Parameters: %teacher%(String), %hi%(String)
整合Mybatis-Spring可以通过xml的方式配置,也可以通过注解配置。配置Mybatis-Spring分为几个部分:配置数据源、配置SqlSessionFactory、配置SqlSessionTemplate、配置Mapper和事务处理。SqlSessionTemplate是对SqlSession操作的封装。
pom.xml导入依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.tyson</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.3.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<mybatis-spring.version>1.3.0</mybatis-spring.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.38</mysql.version>
<mybatis.version>3.4.1</mybatis.version>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<c3p0.version>0.9.1.2</c3p0.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--Spring框架核心库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-spring适配器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis-spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Spring java数据库访问包,在本例中主要用于提供数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql数据库驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis ORM框架 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit单元测试工具 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--c3p0 连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>${c3p0.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--用于包含或排除某些资源-->
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd">
<!--1 引入属性文件,在配置中占位使用 -->
<!--classpath:只会到你的class路径中查找找文件。
classpath*:不仅包含class路径,还包括jar文件中(class路径)进行查找。加载速度较慢-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:db.properties" />
<!--2 配置C3P0数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<!--驱动类名 -->
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<!-- url -->
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<!-- 用户名 -->
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<!-- 密码 -->
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<!-- 当连接池中的连接耗尽的时候c3p0一次同时获取的连接数 -->
<property name="acquireIncrement" value="5"></property>
<!-- 初始连接池大小 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="10"></property>
<!-- 连接池中连接最小个数 -->
<property name="minPoolSize" value="5"></property>
<!-- 连接池中连接最大个数 -->
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="20"></property>
</bean>
<!--3 会话工厂bean sqlSessionFactoryBean -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!-- 别名 -->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.tyson.pojo"></property>
<!-- sql映射文件路径 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:sqlMapConfig.xml"></property>
<!-- 当mybatis的xml文件和mapper接口不在相同包下时,需要用mapperLocations属性指定xml文件的路径。
*是个通配符,代表所有的文件,**代表所有目录下 -->
<!--<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/tyson/mapper/*.xml" />-->
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionTemplate" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<!--自动扫描mapper,Spring上下文自动扫描com.tyson.mapper包中标注了@Repository的接口,自动生成mapper-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.tyson.mapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionTemplateBeanName" value="sqlSessionTemplate"/>
<property name="annotationClass" value="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务-->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--基于注解的声明式事务管理配置-->
<!--MyBatis自动参与到spring事务管理中,无需额外配置,
只要org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean引用的数据源与DataSourceTransactionManager引用的数据源一致即可,
否则事务管理会不起作用。-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
<!--容器自动扫描ioc组件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.tyson"/>
</beans>
sqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties/><!--属性-->
<settings><!--设置-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--允许jdbc生成的键-->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true"/>
<!--配置默认的执行器。SIMPLE执行器没有特别之处;REUSE执行器重用预处理语句;BATCH执行器重用语句和批量更新-->
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="REUSE"/>
<!--全局启用或禁用延迟加载,当禁用时,所有的关联对象都会即时加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--超时时间,它决定驱动等待一个数据库响应的时间-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
实体类Role.java
import java.util.Date;
public class Role {
private Long id;
private String roleName;
private String note;
private Date regTime;
//getter和setter
}
RoleMapper.java
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface RoleMapper {
public void insertRole(Role role);
}
RoleMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper">
<insert id="insertRole" parameterType="role">
insert into role(id, role_name, note) values(#{id}, #{roleName}, #{note})
</insert>
</mapper>
RoleService.java
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
public interface RoleService {
public void insertRole(Role role);
}
RoleServiceImpl.java
import com.tyson.mapper.RoleMapper;
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
import com.tyson.service.RoleService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("roleService")
public class RoleServiceImpl implements RoleService {
@Autowired
RoleMapper roleMapper;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void insertRole(Role role) {
roleMapper.insertRole(role);
}
}
测试
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
import com.tyson.service.RoleService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
public class RoleTest {
@Autowired
RoleService roleService;
@Test
public void insertRolesTest() {
Role role = new Role();
role.setId(1L);
role.setRoleName("stu");
role.setNote("emm");
roleService.insertRole(role);
}
}
Mybatis内置的ExecutorType有3种,默认的是simple,该模式下它为每个语句的执行创建一个新的预处理语句,单条提交sql;而batch模式重复使用已经预处理的语句,并且批量执行所有更新语句。
在数据库中使用批量更新有利于提高性能。在Mybatis中通过修改mybatis-config.xml配置文件中的settings的defaultExecutorType来制定其执行器为批量执行器。
<settings>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="BATCH"/>
</settings>
也可以通过Java代码实现批量执行器的使用。
sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
在Spring中使用批量执行器。
<bean id="sqlSessionTemplate" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
<!--使用批量模式-->
<constructor-arg index="1" value="BATCH"/>
</bean>
使用批量执行器,在默认情况下,它在sqlSession进行commit操作之后才会执行SQL语句。
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void roleTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
Role role = new Role();
role.setNote("emm");
role.setRoleName("man");
roleMapper.insertRole(role);
roleMapper.insertRole(role);
roleMapper.insertRole(role);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
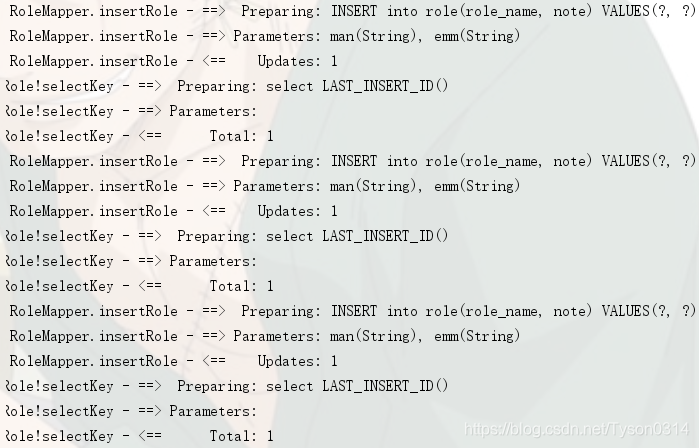
测试结果:
未开启批量执行:
开启批量执行:
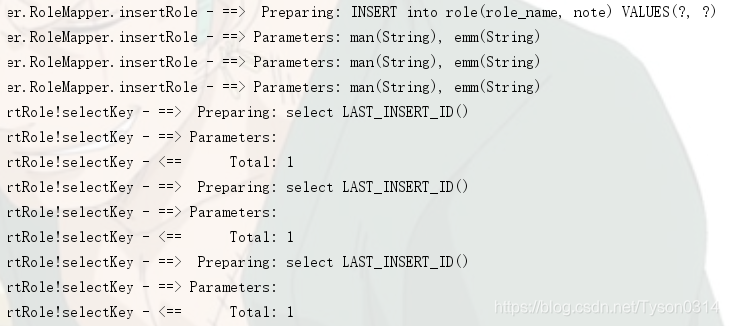
设置ExecutorType.BATCH原理:把SQL语句发给数据库,数据库预编译好,数据库等待需要运行的参数,接收到参数后一次运行,ExecutorType.BATCH只打印一次SQL语句,多次设置参数。
存储过程就是具有名字的一段代码,用来完成一个特定的功能。创建的存储过程保存在数据库的数据字典中。
优点(为什么要用存储过程?):
①将重复性很高的一些操作,封装到一个存储过程中,简化了对这些SQL的调用
②批量处理:SQL+循环,减少流量
1.新建存储过程,按照传入的参数查询男女学生人数。
#声明分隔符,默认为“;",编译器将两个$之间的内容当做存储过程的代码,不会执行这些代码
DELIMITER $
CREATE PROCEDURE gesture_count(IN sex INT, OUT ges_count INT)
BEGIN
IF sex=1 THEN
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student AS s WHERE s.sex='male' INTO ges_count;
ELSE
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student AS s WHERE s.sex='female' INTO ges_count;
END IF;
END
$
#还原分隔符
DELIMITER ;
调用存储过程。
SET @ges_count=1;
CALL gesture_count(2, @ges_count);
SELECT @ges_count
2.定义一个Pojo反映存储过程的参数。
public class ProcedureParam {
private int sex;
private int gesCount;
//setter和getter
}
3.在xml映射器做配置,调用存储过程。
<!--statementType="CALLABLE"表示用存储过程执行它,通过配置mode,mybatis会帮我们回填gesCount-->
<select id="gesCount" parameterType="com.tyson.pojo.ProcedureParam" statementType="CALLABLE">
call gesture_count(
#{sex, mode=IN, jdbcType=INTEGER},
#{gesCount, mode=OUT, jdbcType=INTEGER}
)
</select>
4.存储过程接口。
public void gesCount(ProcedureParam procedureParam);
5.测试代码。
@Test
public void getCountTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try{
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
ProcedureParam procedureParam = new ProcedureParam();
procedureParam.setSex(2);
studentMapper.gesCount(procedureParam);
String sex = procedureParam.getSex() == 1 ? "male" : "female";
log.info("sex: " + sex + " count: " + procedureParam.getGesCount());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
游标可以遍历返回的多行结果。Mysql中游标只适合存储过程和函数。
语法:
1.定义游标:declare cur_name cursor for select 语句;
2.打开游标:open cur_name;
3.获取结果:fetch cur_name into param1, param2, ...;
4.关闭游标:close cur_name;
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS find_customer;
#声明分隔符,默认为“;",编译器将两个$之间的内容当做存储过程的代码,不会执行这些代码
DELIMITER $
CREATE PROCEDURE find_customer()
BEGIN
DECLARE no_more_record INT DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE id VARCHAR(64);
DECLARE cus_name VARCHAR(16);
#声明游标
DECLARE cur CURSOR FOR SELECT * FROM customer;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET no_more_record = 1;
OPEN cur;
FETCH cur INTO id, cus_name;
#不断循环到达表的末尾,继续fetch会报错
WHILE no_more_record != 1 DO
INSERT INTO customer_tmp(id, `name`)
VALUES(id, cus_name);
FETCH cur INTO id, cus_name;
END WHILE;
CLOSE cur;
END
$
#还原分隔符
DELIMITER ;
调用存储过程。
TRUNCATE TABLE customer_tmp;
CALL find_customer();
RowBounds分页是Mybatis内置的基本功能,在任何的select语句中都可以使用,它是在SQL语句查询出所有结果之后,对结果进行截断,当SQL语句返回大量结果时,容易造成内存溢出。其适用于返回数据量小的查询。
RowBounds有两个重要的参数limit和offeset,offeset表示从哪一条记录开始读取,limit表示限制返回的记录数。
下面通过角色名称模糊查询角色信息。
<!--使用resultMap进行结果映射, 用typeHandler对note字段进行转化-->
<select id="getRoleByRoleName" parameterType="string" resultMap="roleMap">
select id, role_name, note, reg_time from role where 1=1
<if test="roleName != null and roleName != ''">
and role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%')
</if>
</select>
RoleMapper接口定义。
import com.tyson.pojo.Role;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
public interface RoleMapper {
public List<Role> getRoleByRoleName(@Param("roleName") String roleName, RowBounds rowBounds);
}
测试代码。
@Test
public void getRoleByRoleNameTest() {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtil.openSqlSession();
RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class);
List<Role> roles = roleMapper.getRoleByRoleName("man", new RowBounds(0, 5));
roles.forEach(role -> {
log.info(role.toString());
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
测试结果返回五条记录。
#{ } 被解析成预编译语句,预编译之后可以直接执行,不需要重新编译sql。
//sqlMap 中如下的 sql 语句
select * from user where name = #{name};
//解析成为预编译语句;编译好SQL语句再取值
select * from user where name = ?;
${ } 仅仅为一个字符串替换,每次执行sql之前需要进行编译,存在 sql 注入问题。
select * from user where name = '${name}'
//传递的参数为 "ruhua" 时,解析为如下,然后发送数据库服务器进行编译。取值以后再去编译SQL语句。
select * from user where name = "ruhua";
数据库接受到sql语句之后,需要词法和语义解析,优化sql语句,制定执行计划。这需要花费一些时间。如果一条sql语句需要反复执行,每次都进行语法检查和优化,会浪费很多时间。预编译语句就是将sql语句中的值用占位符替代,即将sql语句模板化。一次编译、多次运行,省去了解析优化等过程。
mybatis是通过PreparedStatement和占位符来实现预编译的。
mybatis底层使用PreparedStatement,默认情况下,将对所有的 sql 进行预编译,将#{}替换为?,然后将带有占位符?的sql模板发送至mysql服务器,由服务器对此无参数的sql进行编译后,将编译结果缓存,然后直接执行带有真实参数的sql。
预编译的作用:
预编译阶段可以优化 sql 的执行。预编译之后的 sql 多数情况下可以直接执行,数据库服务器不需要再次编译,可以提升性能。
预编译语句对象可以重复利用。把一个 sql 预编译后产生的 PreparedStatement 对象缓存下来,下次对于同一个sql,可以直接使用这个缓存的 PreparedState 对象。
防止SQL注入。使用预编译,而其后注入的参数将不会再进行SQL编译。也就是说其后注入进来的参数系统将不会认为它会是一条SQL语句,而默认其是一个参数。
目前流行的缓存服务器有Redis、Ehcache、MangoDB等。缓存是计算机内存保存的数据,在读取数据的时候不用从磁盘读入,具备快速读取的特点,如果缓存命中率高,可以极大提升系统的性能。若缓存命中率低,则使用缓存意义不大,故使用缓存的关键在于存储内容访问的命中率。
Mybatis对缓存提供支持,默认情况下只开启一级缓存,一级缓存作用范围为同一个SqlSession。在SQL和参数相同的情况下,我们使用同一个SqlSession对象调用同一个Mapper方法,往往只会执行一次SQL。因为在使用SqlSession第一次查询后,Mybatis会将结果放到缓存中,以后再次查询时,如果没有声明需要刷新,并且缓存没超时的情况下,SqlSession只会取出当前缓存的数据,不会再次发送SQL到数据库。若使用不同的SqlSession,因为不同的SqlSession是相互隔离的,不会使用一级缓存。
二级缓存作用范围是Mapper(Namespace),可以使缓存在各个SqlSession之间共享。二级缓存默认不开启,需要在mybatis-config.xml开启二级缓存:
<!-- 通知 MyBatis 框架开启二级缓存 -->
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
并在相应的Mapper.xml文件添加cache标签,表示对哪个mapper 开启缓存:
<cache/>
二级缓存要求返回的POJO必须是可序列化的,即要求实现Serializable接口。
当开启二级缓存后,数据的查询执行的流程就是 二级缓存 -> 一级缓存 -> 数据库。
当调用Mapper接口方法的时候,Mybatis会使用JDK动态代理返回一个Mapper代理对象,代理对象会拦截接口方法,根据接口的全路径和方法名,定位到sql,使用executor执行sql语句,然后将sql执行结果返回。
因为mybatis动态代理寻找策略是 全限定名+方法名,不涉及参数,所以不支持重载。
优点:
缺点:
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。