代码拉取完成,页面将自动刷新
同步操作将从 doocs/leetcode 强制同步,此操作会覆盖自 Fork 仓库以来所做的任何修改,且无法恢复!!!
确定后同步将在后台操作,完成时将刷新页面,请耐心等待。
给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 stones ,数组中的元素 严格递增 ,表示一条河中石头的位置。
一只青蛙一开始在第一块石头上,它想到达最后一块石头,然后回到第一块石头。同时每块石头 至多 到达 一次。
一次跳跃的 长度 是青蛙跳跃前和跳跃后所在两块石头之间的距离。
stones[i] 跳到 stones[j] ,跳跃的长度为 |stones[i] - stones[j]| 。一条路径的 代价 是这条路径里的 最大跳跃长度 。
请你返回这只青蛙的 最小代价 。
示例 1:
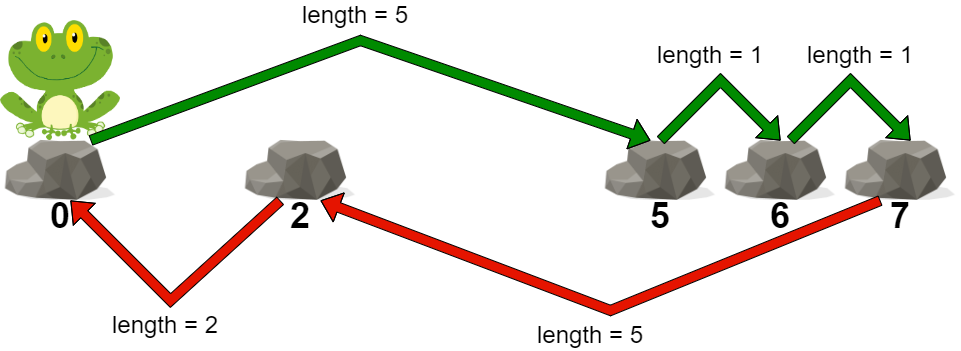
输入:stones = [0,2,5,6,7] 输出:5 解释:上图展示了一条最优路径。 这条路径的代价是 5 ,是这条路径中的最大跳跃长度。 无法得到一条代价小于 5 的路径,我们返回 5 。
示例 2:
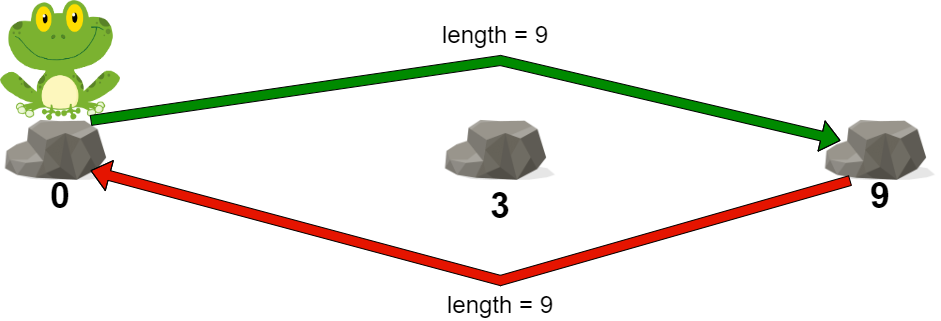
输入:stones = [0,3,9] 输出:9 解释: 青蛙可以直接跳到最后一块石头,然后跳回第一块石头。 在这条路径中,每次跳跃长度都是 9 。所以路径代价是 max(9, 9) = 9 。 这是可行路径中的最小代价。
提示:
2 <= stones.length <= 1050 <= stones[i] <= 109stones[0] == 0stones 中的元素严格递增。要使得跳跃过程中的每一步的最大跳跃长度最小,我们应该将跳跃过程切分成尽可能多的连续的步骤。通过观察,间隔跳跃可以获取最优解。
时间复杂度 $O(n)$,空间复杂度 $O(1)$。其中 $n$ 为数组 stones 的长度。
class Solution:
def maxJump(self, stones: List[int]) -> int:
ans = stones[1] - stones[0]
for i in range(2, len(stones)):
ans = max(ans, stones[i] - stones[i - 2])
return ans
class Solution {
public int maxJump(int[] stones) {
int ans = stones[1] - stones[0];
for (int i = 2; i < stones.length; ++i) {
ans = Math.max(ans, stones[i] - stones[i - 2]);
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int maxJump(vector<int>& stones) {
int ans = stones[1] - stones[0];
for (int i = 2; i < stones.size(); ++i) ans = max(ans, stones[i] - stones[i - 2]);
return ans;
}
};
func maxJump(stones []int) int {
ans := stones[1] - stones[0]
for i := 2; i < len(stones); i++ {
ans = max(ans, stones[i]-stones[i-2])
}
return ans
}
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。