同步操作将从 doocs/leetcode 强制同步,此操作会覆盖自 Fork 仓库以来所做的任何修改,且无法恢复!!!
确定后同步将在后台操作,完成时将刷新页面,请耐心等待。
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 grid ,每个元素都为 非负 整数,其中 grid[row][col] 表示可以访问格子 (row, col) 的 最早 时间。也就是说当你访问格子 (row, col) 时,最少已经经过的时间为 grid[row][col] 。
你从 最左上角 出发,出发时刻为 0 ,你必须一直移动到上下左右相邻四个格子中的 任意 一个格子(即不能停留在格子上)。每次移动都需要花费 1 单位时间。
请你返回 最早 到达右下角格子的时间,如果你无法到达右下角的格子,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:
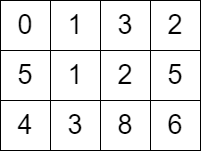
输入:grid = [[0,1,3,2],[5,1,2,5],[4,3,8,6]] 输出:7 解释:一条可行的路径为: - 时刻 t = 0 ,我们在格子 (0,0) 。 - 时刻 t = 1 ,我们移动到格子 (0,1) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[0][1] <= 1 。 - 时刻 t = 2 ,我们移动到格子 (1,1) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][1] <= 2 。 - 时刻 t = 3 ,我们移动到格子 (1,2) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][2] <= 3 。 - 时刻 t = 4 ,我们移动到格子 (1,1) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][1] <= 4 。 - 时刻 t = 5 ,我们移动到格子 (1,2) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][2] <= 5 。 - 时刻 t = 6 ,我们移动到格子 (1,3) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][3] <= 6 。 - 时刻 t = 7 ,我们移动到格子 (2,3) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[2][3] <= 7 。 最终到达时刻为 7 。这是最早可以到达的时间。
示例 2:
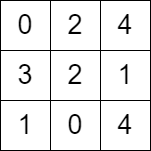
输入:grid = [[0,2,4],[3,2,1],[1,0,4]] 输出:-1 解释:没法从左上角按题目规定走到右下角。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 1050 <= grid[i][j] <= 105grid[0][0] == 0我们观察发现,如果在格子 $(0, 0)$ 处无法移动,即 $grid[0][1] \gt 1$ 且 $grid[1][0] \gt 1$,那么我们在格子 $(0, 0)$ 无法再移动,此时返回 $-1$ 即可。而对于其他情况,我们都可以移动。
接下来,我们定义 $dist[i][j]$ 表示 $(i, j)$ 处的最早到达时间,初始时 $dist[0][0] = 0$,而其他位置的 $dist$ 均初始化为 $\infty$。
我们使用优先队列(小根堆)来维护当前可以移动的格子,优先队列中的元素为 $(dist[i][j], i, j)$,即 $(dist[i][j], i, j)$ 表示 $(i, j)$ 处的最早到达时间。
我们每次从优先队列中取出当前最早到达的格子 $(t, i, j)$,如果 $(i, j)$ 为 $(m - 1, n - 1)$,那么我们直接返回 $t$ 即可,否则,我们遍历 $(i, j)$ 的上下左右四个相邻格子 $(x, y)$,如果 $t + 1 \lt grid[x][y]$,那么我们移动到 $(x, y)$ 的时间 $nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - (t + 1)) \bmod 2$,此时我们可以通过反复移动将时间拉长至不小于 $grid[x][y]$,这取决于 $t + 1$ 和 $grid[x][y]$ 距离的奇偶性。否则,我们移动到 $(x, y)$ 的时间 $nt = t + 1$。如果 $nt \lt dist[x][y]$,那么我们更新 $dist[x][y] = nt$,并将 $(nt, x, y)$ 加入优先队列中。
时间复杂度 $O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n))$,空间复杂度 $O(m \times n)$。其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别为网格的行数和列数。
class Solution:
def minimumTime(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if grid[0][1] > 1 and grid[1][0] > 1:
return -1
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dist = [[inf] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[0][0] = 0
q = [(0, 0, 0)]
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
while 1:
t, i, j = heappop(q)
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return t
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n:
nt = t + 1
if nt < grid[x][y]:
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - nt) % 2
if nt < dist[x][y]:
dist[x][y] = nt
heappush(q, (nt, x, y))
class Solution {
public int minimumTime(int[][] grid) {
if (grid[0][1] > 1 && grid[1][0] > 1) {
return -1;
}
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (var e : dist) {
Arrays.fill(e, 1 << 30);
}
dist[0][0] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
pq.offer(new int[] {0, 0, 0});
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (true) {
var p = pq.poll();
int i = p[1], j = p[2];
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return p[0];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
int nt = p[0] + 1;
if (nt < grid[x][y]) {
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - nt) % 2;
}
if (nt < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = nt;
pq.offer(new int[] {nt, x, y});
}
}
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int minimumTime(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
if (grid[0][1] > 1 && grid[1][0] > 1) {
return -1;
}
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int dist[m][n];
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[0][0] = 0;
using tii = tuple<int, int, int>;
priority_queue<tii, vector<tii>, greater<tii>> pq;
pq.emplace(0, 0, 0);
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (1) {
auto [t, i, j] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return t;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
int nt = t + 1;
if (nt < grid[x][y]) {
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - nt) % 2;
}
if (nt < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = nt;
pq.emplace(nt, x, y);
}
}
}
}
}
};
func minimumTime(grid [][]int) int {
if grid[0][1] > 1 && grid[1][0] > 1 {
return -1
}
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dist := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = 1 << 30
}
}
dist[0][0] = 0
pq := hp{}
heap.Push(&pq, tuple{0, 0, 0})
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for {
p := heap.Pop(&pq).(tuple)
i, j := p.i, p.j
if i == m-1 && j == n-1 {
return p.t
}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
nt := p.t + 1
if nt < grid[x][y] {
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y]-nt)%2
}
if nt < dist[x][y] {
dist[x][y] = nt
heap.Push(&pq, tuple{nt, x, y})
}
}
}
}
}
type tuple struct{ t, i, j int }
type hp []tuple
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].t < h[j].t }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(tuple)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。