A html parser with xpath base on Jsoup and Antlr4.Maybe it is the best in java,Just try it.
JsoupXpath is a pure Java-developed parser that uses xpath to parse and extract html data. It completely re-implements the W3C XPATH 1.0 standard syntax for html parsing, the Lexer and Parser of xpath are built based on Antlr4, and the html DOM tree generation uses Jsoup, so named JsoupXpath. JsoupXpath was developed in the condition that we could not find a xpath parser which is good enough, but also wanted to take advantage of the powerful ability and convenience of xpath in java. The implementation logic of JsoupXpath is clear and easy to extend, it supports the complete W3C XPATH 1.0 standard syntax. W3C specifications: http: //www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-xpath-19991116, JsoupXpath syntax description file: Xpath.g4
https://github.com/zhegexiaohuozi/JsoupXpath/releases
Any questions or suggestions can be discussed by sending an email to the following mailing list. Before your first speech, you need to subscribe and wait for approval. (mainly used to block advertising, etc.)
Maven dependencies, please refer to the release information or the central maven repository for the full version:
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.wanghaomiao</groupId>
<artifactId>JsoupXpath</artifactId>
<version>${latest-version-in-maven}</version>
</dependency>
String html = "<html><body><script>console.log('aaaaa')</script><div class='test'>some body</div><div class='xiao'>Two</div></body></html>";
JXDocument underTest = JXDocument.create(html);
String xpath = "//div[contains(@class,'xiao')]/text()";
JXNode node = underTest.selNOne(xpath);
Assert.assertEquals("Two",node.asString());
Others can refer to org.seimicrawler.xpath.JXDocumentTest, there are a lot of test cases here.
Or a more typical example in Issue.
Supports complete W3C XPATH 1.0 standard syntax. W3C specifications: http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-xpath-19991116
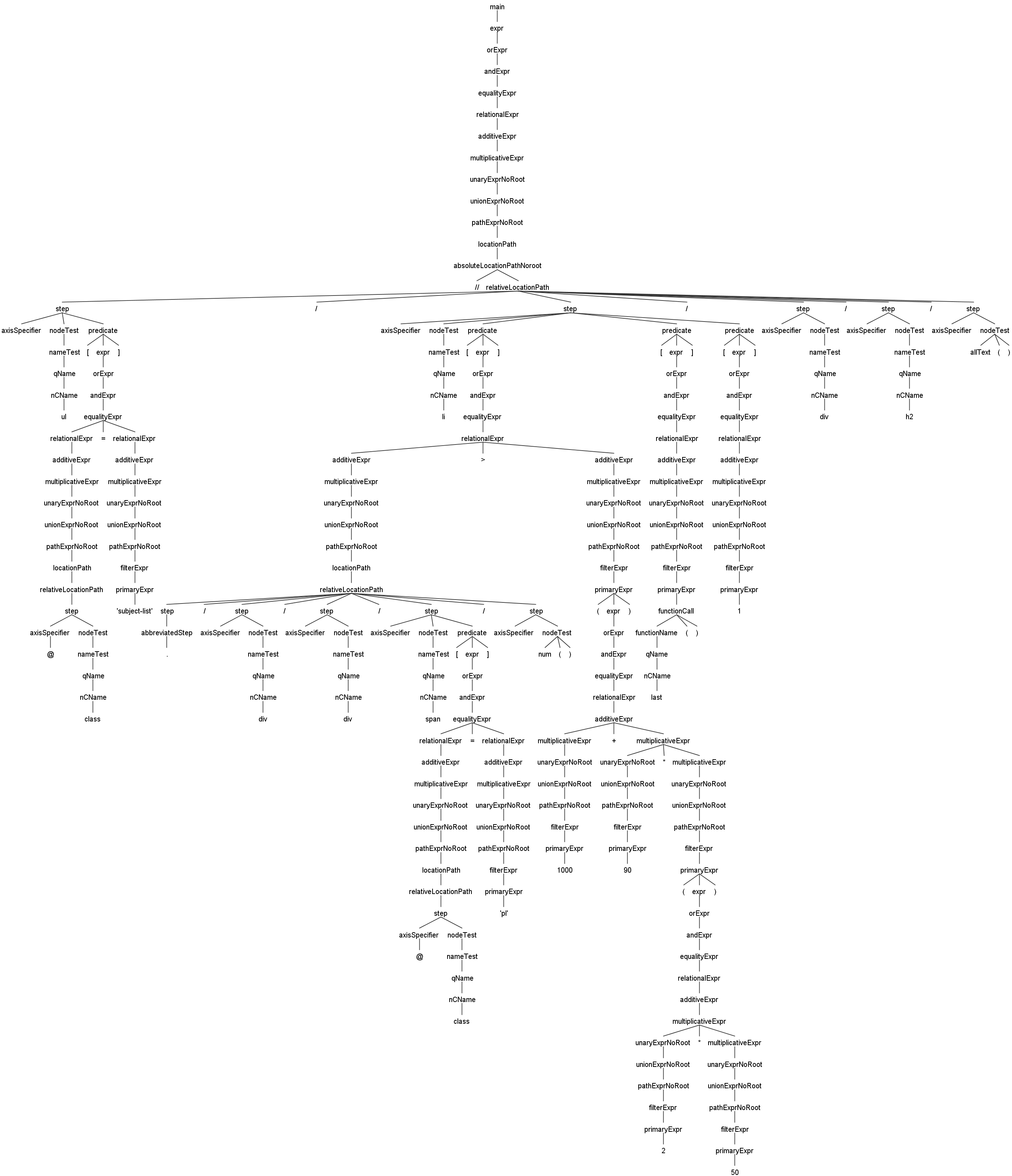
//ul[@class='subject-list']/li[./div/div/span[@class='pl']/num()>(1000+90*(2*50))][last()][1]/div/h2/allText()
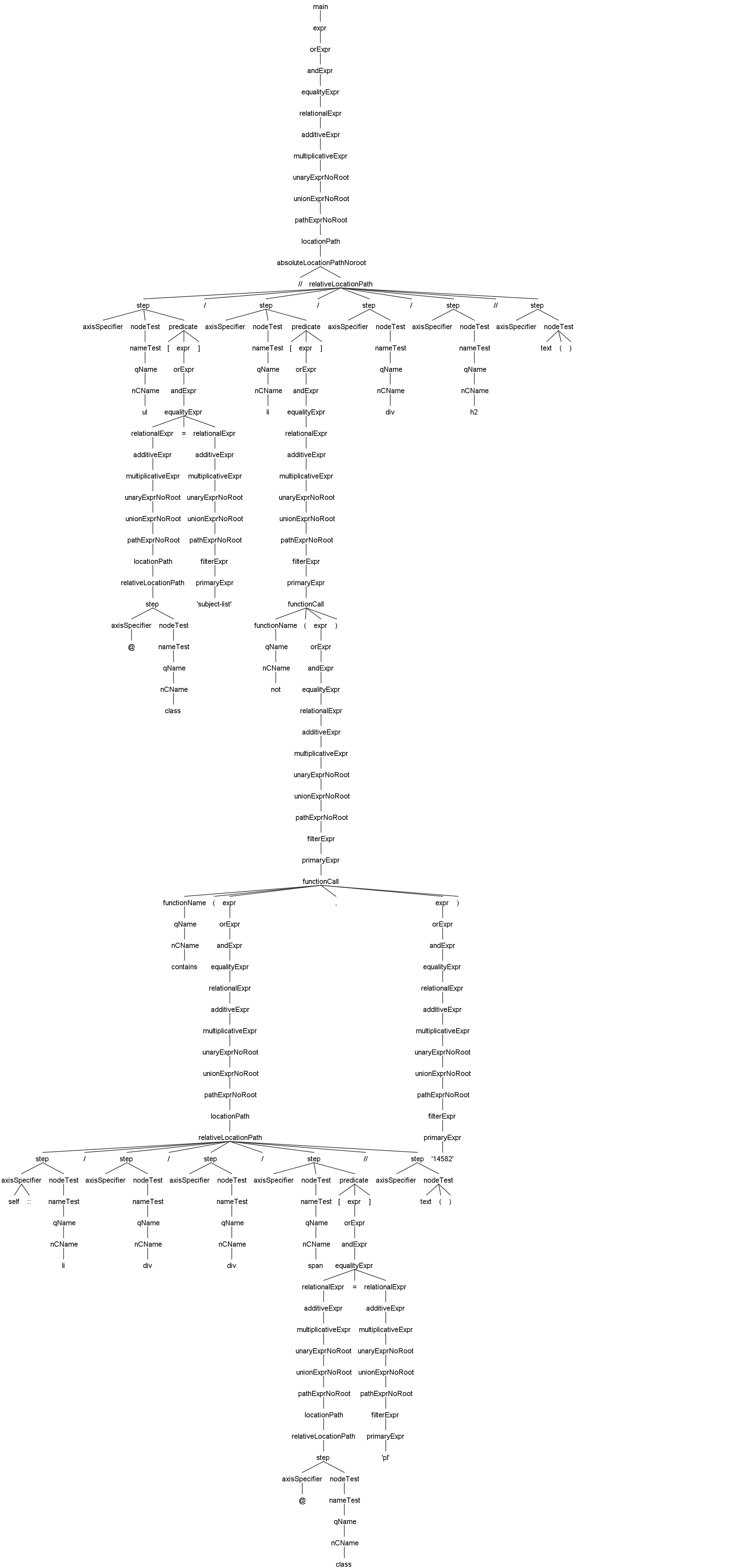
//ul[@class='subject-list']/li[not(contains(self::li/div/div/span[@class='pl']//text(),'14582'))]/div/h2//text()
In most cases, it is not recommended to directly paste the Xpath generated in Firefox or chrome. These browsers always automatically complete some tags according to the standard in render page. For example, the table tag is automatically added with the tbody tag, it’s obviously that the generated Xpath path is not the most versatile, and so the value is very likely cannot be taken. Therefore, to use Xpath and feel the convenience and elegance it brings, it is best to learn the standard syntax of Xpath so that you can handle all kinds of problems with ease and enjoy the true power of Xpath!
int position() returns the position of the current node in context
int last() returns the last node position of the context
int first() returns the first node position of the context
string concat(string, string, string*) concatenate several strings
boolean contains(string, string) determines whether the first string contains the second
int count(node-set) counts the number of nodes in a given set of nodes
double/long sum(node-set) the sum function returns the sum, for each node in the argument node-set, of the result of converting the string-values of the node to a number
boolean starts-with(string, string) determines whether the first string starts with the second
int string-length(string?) returns the string length if a string is given, if not, converts the current node to a string and returns the length
string substring(string, number, number?) The first parameter specifies the string, the second specifies the starting position (xpath indexes all start from 1), and the third specifies the length to be truncated. Here we must pay attention to the syntax of xpath, this is not the end position.
substring("12345", 1.5, 2.6) returns "234"
substring("12345", 2, 3) returns "234"
string substring-ex(string, number, number) The first parameter specifies the string, the second specifies the starting position (java indexes are used to start from 0), and the third specifies the ending position (supports negative numbers). This is JsoupXpath extended functions, convenient for developers who are used to java.
string substring-after(string, string) truncate the part after the second string in the first string
string substring-before(string, string) truncate the part after the position that the second string last occurred in the first string
The above functions are just the standard functions in the Xpath 1.0. Developers can also add custom functions quickly and easily, just need to implement the interface org.seimicrawler.xpath.core.Function.java, and call Scanner.registerFunction ( Class <? Extends Function> func) when your system is initialized. It’s no need to modify the syntax paradigm for JsoupXpath can recognize and load at runtime. You are welcome to submit a pull request to the main repository about functions in the standard syntax which are not implemented by JsoupXpath yet.
allText() extracts all text under the node, instead of recursive text usage like // div / h3 // text ()html() get the internal html of all nodesouterHtml() gets all html of all nodes including the node itselfnum() extracts all the numbers in the node's own text. If you know that there is only one number in the node's own text (the text contained in the non-children's nodes), such as the number of reads, the number of comments, and the price, you can directly extract it. If there are multiple numbers, the first matching consecutive number will be extracted.text() extracts the node's own textnode() extract all nodesAxisName: 'ancestor' // Select from the ancestors of the node in the current context
| 'ancestor-or-self' // Select from the ancestors of the node and the node itself in the current context
| 'attribute' // Operations for extracting node attributes
| 'child' // Select from the child nodes of the node in the current context. This is the default axis of xpath. For example, /div/li is the shorthand of /div/child::li
| 'descendant' // Select from the descendants of the node in the current context
| 'descendant-or-self' // Select from the descendants of the node and the node itself in the current context
| 'following' // Select from all nodes behind the node in the current context
| 'following-sibling' // Select from all sibling nodes behind the node in the current context
| parent ' // Select from the parent of the node in the current context
| 'preceding' // Select from all nodes before the node in the current context
| 'preceding-sibling' // Select from all sibling nodes before the node in the current context
| 'self' // Select in current context
| 'following-sibling-one' // Select from the following sibling node of the node in the context (JsoupXpath expansion)
| 'preceding-sibling-one' // Select the preceding sibling node of the node in the context (JsoupXpath extension)
| 'sibling' // All siblings (JsoupXpath extension) (under development ...)
;
MINUS
: '-';
PLUS
: '+';
DOT
: '.';
MUL
: '*';
DIVISION
: '`div`';
MODULO
: '`mod`';
DOTDOT
: '..';
AT
: '@';
COMMA
: ',';
PIPE
: '|';
LESS
: '<';
MORE_
: '>';
LE
: '<=';
GE
: '>=';
START_WITH
: '^='; // `a^=b` a startwith b (JsoupXpath extension)
END_WITH
: '$='; // `a*=b` a contains b (JsoupXpath extension)
CONTAIN_WITH
: '*='; // a contains b (JsoupXpath extension)
REGEXP_WITH
: '~='; // the content of a matches the regular expression b (JsoupXpath extension)
REGEXP_NOT_WITH
: '!~'; // the content of a does not match the regular expression b (JsoupXpath extension)
Currently, JsoupXpath is widely used in projects or organizations such as SeimiCrawler. If you also have a project using JsoupXpath and want to appear in this list, you can contact me through the following contact details, the mail format can be:
Project or organization name: XX
Project or organization URL: http://xxx.xxx.cc
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。